GLP-1 Weight Loss Programs: Complete Beginner’s Guide for 2026

GLP-1 Weight Loss Programs: Complete Beginner’s Guide for 2026
GLP-1 weight loss programs use medications that mimic a natural hormone your body produces to regulate appetite and blood sugar, producing 10-22% average body weight loss, results previously only achievable through bariatric surgery.
If you’re considering GLP-1 therapy but feeling overwhelmed by information about Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and other options, this comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know to make informed decisions about starting treatment.
GLP-1 medications have revolutionized weight loss treatment by addressing the biological mechanisms that make weight loss difficult. Rather than relying solely on willpower and calorie restriction, these medications work with your body’s natural hunger and satiety signals to make sustainable weight loss achievable.
TrimRx provides accessible GLP-1 therapy through licensed providers, offering both compounded semaglutide at $199/month and compounded tirzepatide at $349/month with complete medical support.
Key Takeaways:
- GLP-1 medications produce 10-22% average body weight loss over 16-20 months
- Weekly injections using small needles are easier than most people expect
- Side effects like nausea are common initially but typically improve within 4-8 weeks
- Long-term use is necessary to maintain weight loss results
- Compounded options make effective treatment affordable ($199-$349/month vs $1,000+)
- Telehealth access allows you to start treatment entirely online without in-person visits
What Are GLP-1 Medications?
GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) medications are a class of drugs that mimic a natural hormone your intestines produce after eating, helping regulate appetite, blood sugar, and metabolism.
The Science Behind GLP-1:
Natural GLP-1 Hormone:
Your body naturally produces GLP-1 in your intestines when you eat. This hormone:
- Signals your brain that you’re full and satisfied
- Tells your pancreas to release insulin to manage blood sugar
- Slows down how quickly food leaves your stomach
- Reduces appetite and food cravings
- Helps prevent your liver from releasing excess glucose
The Problem: Natural GLP-1 only lasts a few minutes before enzymes break it down. It works while you’re eating and shortly after, but the effects disappear quickly.
GLP-1 Medications Are Different:
Pharmaceutical GLP-1 medications are synthetic versions engineered to:
- Last much longer in your body (days instead of minutes)
- Resist breakdown by enzymes
- Maintain therapeutic levels continuously
- Produce stronger, sustained effects than natural GLP-1
Think of it this way:
- Natural GLP-1: Brief “I’m full” signal during meals
- GLP-1 medications: Continuous “you’re satisfied, don’t overeat” signal all week
Types of GLP-1 Medications:
Pure GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These activate only GLP-1 receptors:
Semaglutide:
- Brand names: Wegovy (weight loss), Ozempic (diabetes)
- Dosing: Once weekly injection
- Average weight loss: 10-15% of body weight
- FDA approved: 2017 (Ozempic), 2021 (Wegovy)
Liraglutide:
- Brand name: Saxenda (weight loss), Victoza (diabetes)
- Dosing: Daily injection
- Average weight loss: 5-8% of body weight
- Older, less effective than semaglutide
Dulaglutide:
- Brand name: Trulicity
- Dosing: Once weekly injection
- Primarily for diabetes, not typically used for weight loss
Dual GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Agonist:
Tirzepatide:
- Brand names: Zepbound (weight loss), Mounjaro (diabetes)
- Dosing: Once weekly injection
- Average weight loss: 15-22% of body weight
- FDA approved: 2022 (Mounjaro), 2023 (Zepbound)
- Most effective weight loss medication available
What Makes Tirzepatide Different:
Tirzepatide activates two hormone receptors instead of one:
GLP-1 Effects (same as semaglutide):
- Appetite suppression
- Slowed stomach emptying
- Increased insulin secretion
- Reduced glucagon production
Plus GIP Effects:
- Enhanced insulin response
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Effects on fat metabolism
- Additional appetite suppression
Result: 5-7% more weight loss than semaglutide alone, making tirzepatide the most effective option.
How GLP-1 Medications Differ from Other Weight Loss Drugs:
Traditional Weight Loss Medications:
- Stimulants (phentermine): Increase energy, suppress appetite through adrenaline-like effects
- Fat blockers (orlistat): Prevent fat absorption in intestines
- Combination pills (Contrave, Qsymia): Multiple mechanisms, moderate effectiveness
These produce 3-9% average weight loss at best.
GLP-1 Medications:
- Work with natural hunger hormones
- Multiple complementary mechanisms
- Target biological causes of overeating
- Produce 10-22% average weight loss
- Much more effective than traditional options
Medical Uses:
FDA-Approved Indications:
For Type 2 Diabetes:
- All GLP-1 medications originally approved for diabetes
- Improve blood sugar control
- Reduce A1C by 1-2 percentage points
- Lower risk of cardiovascular events
For Chronic Weight Management:
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): Approved 2021
- Tirzepatide (Zepbound): Approved 2023
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): Approved 2014
Requirements for weight loss approval:
- BMI ≥30, or
- BMI ≥27 with weight-related condition (diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, etc.)
Off-Label Use:
Many doctors prescribe diabetes versions (Ozempic, Mounjaro) off-label for weight loss because:
- Identical medication to weight loss versions
- Sometimes better insurance coverage
- Same effectiveness regardless of indication on label
This is legal and common medical practice.
Common Brand Names Explained:
The same medication often has multiple brand names:
Semaglutide = Multiple Brands:
- Wegovy: Weight loss indication
- Ozempic: Diabetes indication
- Rybelsus: Oral tablet for diabetes (less effective)
Tirzepatide = Multiple Brands:
- Zepbound: Weight loss indication
- Mounjaro: Diabetes indication
The medication is identical—only the labeled indication differs.
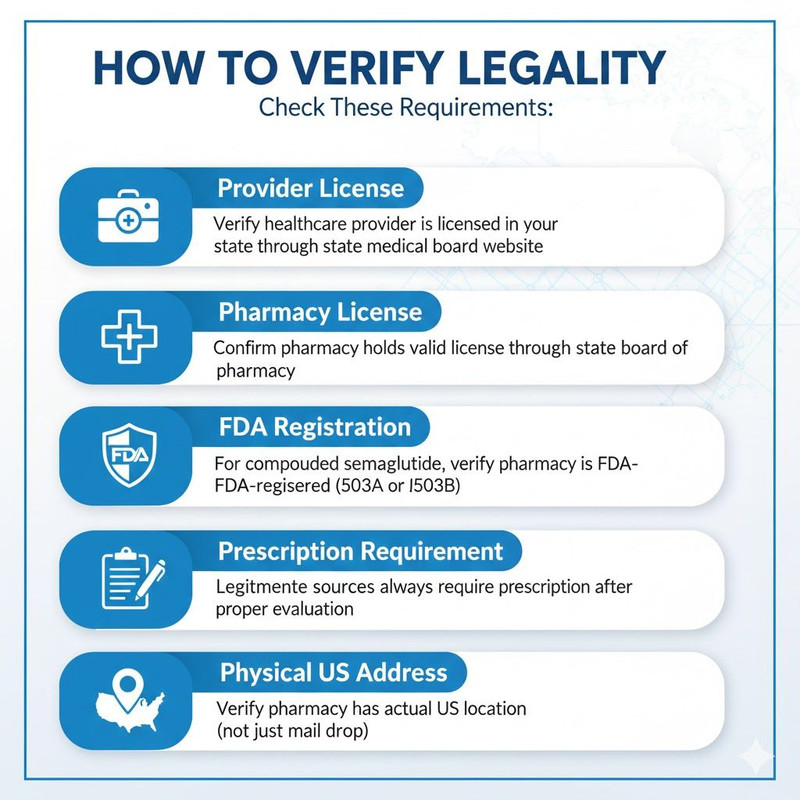
Compounded GLP-1 Medications:
What “Compounded” Means:
Licensed pharmacies can prepare GLP-1 medications from pharmaceutical-grade ingredients:
- Same active ingredient as brand-name
- Made by FDA-registered compounding pharmacies
- Follows strict sterile compounding standards
- Much more affordable ($199-$349/month vs $1,000+)
Legal Status:
- Completely legal when FDA-registered pharmacies prepare them
- Permitted because brand-name versions are on FDA shortage list
- Require valid prescription from licensed provider
Effectiveness:
- Same active ingredient = same effectiveness
- Clinical results identical to brand-name when properly compounded
TrimRx provides access to compounded options that make effective GLP-1 therapy affordable for cash-pay patients.
Why GLP-1 Medications Work So Well:
They Address the Real Problem:
Most weight loss approaches fail because they fight against your body’s biology:
- Calorie restriction triggers stronger hunger signals
- Your metabolism slows to conserve energy
- Cravings intensify as weight decreases
- Willpower alone can’t overcome these biological responses
GLP-1 medications work with your biology:
- Reduce hunger signals at the source
- Increase natural satiety after eating
- Decrease food cravings and obsessive food thoughts
- Make portion control feel natural, not forced
This is why GLP-1 therapy produces results that calorie restriction alone cannot achieve.
The Revolution in Obesity Treatment:
Before GLP-1 Medications:
- Diet and exercise alone: 3-5% sustained weight loss
- Older medications: 3-7% weight loss
- Bariatric surgery: 15-30% weight loss
- Gap between medication and surgery
After GLP-1 Medications:
- Semaglutide: 10-15% weight loss
- Tirzepatide: 15-22% weight loss
- Bridge the gap with non-surgical option
- Results rival some bariatric procedures
GLP-1 therapy has fundamentally changed what’s possible with medical weight loss treatment.
Understanding the best weight loss medications helps you see how GLP-1s compare to all available options.
How GLP-1 Therapy Works for Weight Loss
GLP-1 medications produce weight loss through multiple coordinated mechanisms affecting hunger, digestion, metabolism, and brain signaling.
Mechanism 1: Brain Appetite Regulation
Where It Works: GLP-1 receptors exist throughout your brain, particularly in the hypothalamus—your brain’s appetite control center.
What Happens:
- GLP-1 medications cross the blood-brain barrier
- Activate receptors in appetite control regions
- Reduce hunger signals
- Increase satiety (feeling of fullness)
- Decrease reward response to food
- Reduce obsessive thoughts about food
What You Experience:
- Less frequent hunger
- Feel satisfied with smaller portions
- Don’t think about food constantly
- Reduced cravings for specific foods
- Easier to say no to unnecessary eating
This is the primary mechanism—you naturally eat less because you genuinely want less food.
Mechanism 2: Slowed Gastric Emptying
Where It Works: GLP-1 receptors in your stomach and intestines.
What Happens:
- Food stays in your stomach longer
- Slower movement from stomach to intestines
- Extended digestion time
- Prolonged feeling of fullness after eating
What You Experience:
- Stay full for 3-4 hours after meals instead of 1-2 hours
- Don’t need to snack between meals
- Smaller portions satisfy you
- Physical sensation of fullness lasts longer
Some people describe it as feeling like they ate a large meal even when they only ate a small amount.
Mechanism 3: Blood Sugar Regulation
Where It Works: GLP-1 receptors in your pancreas and liver.
What Happens:
- Increases insulin secretion when blood sugar rises
- Improves how effectively your cells respond to insulin
- Decreases glucagon (hormone that raises blood sugar)
- Reduces glucose production in liver
What You Experience:
- More stable blood sugar levels throughout day
- Fewer energy crashes
- Less reactive hunger from blood sugar drops
- Reduced cravings for sugary foods
Even if you don’t have diabetes, better blood sugar control reduces hunger and makes weight loss easier.
Mechanism 4: Metabolic Improvements
Where It Works: Throughout your body’s metabolic systems.
What Happens:
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Better fat metabolism
- Reduced inflammation
- Positive effects on lipid profiles
- Lower blood pressure
- Cardiovascular benefits
What You Experience:
- More energy
- Better exercise tolerance
- Improved lab markers (cholesterol, triglycerides)
- Reduced risk of metabolic diseases
These effects contribute to overall health improvement beyond just weight loss.
How Tirzepatide’s Dual Mechanism Works:
GIP (Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide) Adds:
Tirzepatide activates both GLP-1 and GIP receptors. The GIP component adds:
Enhanced Insulin Response:
- Even stronger blood sugar control than GLP-1 alone
- Better insulin secretion timing
- Improved insulin sensitivity in tissues
Fat Metabolism Effects:
- GIP receptors exist in fat tissue
- May influence how body stores and uses fat
- Potentially increases fat burning
Synergistic Appetite Suppression:
- GIP and GLP-1 together produce greater appetite reduction
- More potent satiety signals
- Stronger overall effect
This explains why tirzepatide produces 5-7% more weight loss than semaglutide—the dual action is more powerful than GLP-1 alone.
Timeline of How GLP-1s Work:
Week 1-2:
- Medication reaches therapeutic levels
- Begin noticing reduced appetite
- Food sounds less appealing
- Easier to stop eating when satisfied
Week 3-4:
- Appetite suppression more pronounced
- Portions naturally smaller
- Less frequent eating
- First measurable weight loss (3-5 pounds)
Week 5-12:
- Steady appetite control
- Consistent portion reduction
- Weight loss accelerates (1-2 pounds weekly)
- Side effects typically improving
Month 4-6:
- Dose increases continue (if tolerating well)
- Sustained weight loss (10-15 pounds total)
- New eating habits feeling normal
- Significant results becoming visible
Month 7-12:
- Approaching or reaching maintenance dose
- Steady continued weight loss
- Total loss: 15-30 pounds depending on starting weight
- Metabolic improvements evident in lab work
Month 13-20:
- Maximum weight loss achieved
- Average 10-22% total body weight lost
- Maintenance phase begins
- Focus shifts to sustaining results
What GLP-1s DON’T Do:
Common Misconceptions:
They don’t:
- ✗ “Burn fat” directly like thermogenic supplements
- ✗ Block calorie absorption like fat blockers
- ✗ Speed up metabolism dramatically
- ✗ Work without you eating less (you eat less naturally)
- ✗ Cure obesity (stopping leads to weight regain)
- ✗ Eliminate need for healthy habits
They do:
- ✓ Make eating less feel natural and sustainable
- ✓ Reduce biological hunger signals
- ✓ Help you consume fewer calories without constant struggle
- ✓ Provide biological support for behavioral changes
- ✓ Treat obesity as the chronic condition it is
Why GLP-1s Succeed Where Other Approaches Fail:
The Biological Barrier:
When you lose weight through calorie restriction alone:
- Your body produces more hunger hormone (ghrelin)
- Satiety hormones (leptin, GLP-1) decrease
- Metabolism slows by 15-20%
- Cravings intensify
- Your body fights to regain weight
This is why 80-95% of people who lose weight through diet alone regain it.
GLP-1 Medications Break This Cycle:
- Override increased hunger signals
- Maintain satiety despite calorie deficit
- Blunt metabolic adaptation
- Reduce intensity of cravings
- Support sustained weight loss
This is biological support, not just willpower.
Combining GLP-1 with Lifestyle Changes:
GLP-1 Medications Work Best When Combined With:
Nutrition:
- High-protein meals (20-30g per meal)
- Plenty of vegetables and fiber
- Adequate hydration
- Avoiding trigger foods that worsen nausea
Physical Activity:
- Regular walking (30 minutes daily)
- Strength training (2-3x weekly to preserve muscle)
- Movement that you enjoy and will sustain
- Gradually increasing as weight decreases
Behavioral Changes:
- Mindful eating practices
- Stress management
- Adequate sleep (7-9 hours)
- Support system
GLP-1 medications make these changes easier by reducing hunger and cravings, but the lifestyle changes enhance results and improve overall health.
Realistic Expectations:
GLP-1 Therapy Is Not:
- A quick fix
- A substitute for healthy habits
- A cure for obesity
- Without side effects
- Effective for everyone
GLP-1 Therapy Is:
- The most effective weight loss medication available
- Biologically based treatment for chronic disease
- Effective when combined with lifestyle changes
- Generally well-tolerated despite common side effects
- Successful for 85-95% of patients who try it
Understanding how semaglutide compares to tirzepatide helps you choose which GLP-1 medication is right for you.
Available GLP-1 Medications: Complete Overview
Several GLP-1 and dual agonist medications are available, each with different dosing, effectiveness, and cost profiles.
Semaglutide (Wegovy, Ozempic):
Overview:
- Class: GLP-1 receptor agonist
- Administration: Once-weekly subcutaneous injection
- Average Weight Loss: 10-15% of body weight
- FDA Approval: Ozempic (2017), Wegovy (2021)
Available Doses:
- Starting: 0.25 mg weekly
- Escalation: 0.5 mg, 1.0 mg, 1.7 mg
- Maximum: 2.4 mg weekly for weight loss
Clinical Trial Results (STEP-1):
- Average weight loss: 14.9% over 68 weeks
- ≥5% weight loss: 86.4% of participants
- ≥10% weight loss: 69.1% of participants
- ≥15% weight loss: 50.5% of participants
Brand Options:
- Wegovy: FDA-approved for weight loss, $1,349/month
- Ozempic: FDA-approved for diabetes, prescribed off-label for weight loss, $969/month
- Compounded semaglutide: $199-$599/month, same active ingredient
Pros:
- Highly effective (10-15% weight loss)
- Proven cardiovascular benefits (20% reduction in heart attacks/strokes)
- Extensive safety data (on market since 2017)
- Once-weekly convenience
- Affordable compounded option available
Cons:
- Nausea in 44% of users (usually improves)
- Brand-name very expensive without insurance
- Periodic shortages affecting availability
Best For:
- Patients needing to lose 20-50 pounds
- Those with cardiovascular disease (proven benefits)
- Budget-conscious patients (compounded at $199/month)
- Anyone wanting highly effective, proven medication
Tirzepatide (Zepbound, Mounjaro):
Overview:
- Class: Dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist
- Administration: Once-weekly subcutaneous injection
- Average Weight Loss: 15-22% of body weight
- FDA Approval: Mounjaro (2022), Zepbound (2023)
Available Doses:
- Starting: 2.5 mg weekly
- Escalation: 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 12.5 mg
- Maximum: 15 mg weekly for weight loss
Clinical Trial Results (SURMOUNT-1):
- Average weight loss: 22.5% over 72 weeks (15 mg dose)
- ≥5% weight loss: 96% of participants
- ≥10% weight loss: 89% of participants
- ≥15% weight loss: 78% of participants
- ≥20% weight loss: 63% of participants
Brand Options:
- Zepbound: FDA-approved for weight loss, $1,069/month
- Mounjaro: FDA-approved for diabetes, prescribed off-label for weight loss, $1,069/month
- Compounded tirzepatide: $349-$699/month, same active ingredient
Pros:
- Most effective weight loss medication available (15-22% loss)
- Lower nausea rates than semaglutide despite higher potency
- Best chance of achieving 20%+ weight loss
- Affordable compounded option available
Cons:
- More expensive than semaglutide (both brand and compounded)
- Newer medication (less long-term safety data than semaglutide)
- Cardiovascular outcomes trial still ongoing
Best For:
- Patients needing maximum weight loss (50+ pounds)
- Those who plateaued on semaglutide
- Anyone wanting most effective medication available
- Patients who can afford $349/month for compounded option
Liraglutide (Saxenda, Victoza):
Overview:
- Class: GLP-1 receptor agonist
- Administration: Daily subcutaneous injection
- Average Weight Loss: 5-8% of body weight
- FDA Approval: Victoza (2010), Saxenda (2014)
Available Dose:
- Escalate to 3.0 mg daily
Clinical Trial Results (SCALE):
- Average weight loss: 8.0% over 56 weeks
- Significantly less effective than newer GLP-1s
Cost:
- $1,400/month
- No compounded options available
Pros:
- Proven safety record (on market since 2010)
Cons:
- Daily injections (less convenient)
- Much less effective than semaglutide or tirzepatide
- More expensive than more effective options
- Largely obsolete now that better options exist
Verdict: Rarely prescribed anymore. Semaglutide and tirzepatide have largely replaced liraglutide due to superior effectiveness and once-weekly dosing.
Other GLP-1 Medications:
Dulaglutide (Trulicity):
- Once-weekly GLP-1 agonist
- FDA-approved for diabetes only
- Not typically prescribed for weight loss
- Modest weight loss (3-5 kg average)
Exenatide (Byetta, Bydureon):
- Older GLP-1 agonist
- Daily or weekly depending on formulation
- Less effective than newer options
- Rarely used now
Oral Semaglutide (Rybelsus):
- Daily tablet form of semaglutide
- Much less effective than injectable (3-5% weight loss)
- Strict dosing requirements (empty stomach, wait 30 minutes)
- Not recommended for weight loss
Side-by-Side Comparison:
| Feature | Semaglutide | Tirzepatide | Liraglutide |
| Dosing | Weekly | Weekly | Daily |
| Weight Loss | 10-15% | 15-22% | 5-8% |
| Nausea Rate | 44% | 30-37% | 25% |
| Brand Cost | $1,349/mo | $1,069/mo | $1,400/mo |
| Compounded Cost | $199-$599 | $349-$699 | Not available |
| Time on Market | 8 years | 3 years | 15 years |
| CV Benefits | Proven | Being studied | None proven |
| Effectiveness Rank | #2 | #1 | #3 |
Which GLP-1 Should You Choose?
Choose Tirzepatide If:
- Want maximum weight loss results
- Need to lose 50+ pounds
- Can afford $349/month (compounded)
- Want best medication available
Choose Semaglutide If:
- Want excellent results at lowest cost
- Need to lose 20-50 pounds
- Have cardiovascular disease
- Budget is primary concern ($199/month compounded)
Avoid Liraglutide:
- Daily injections inconvenient
- Much less effective than alternatives
- More expensive despite worse results
- No advantage over semaglutide or tirzepatide
Compounded vs Brand-Name:
Same Effectiveness:
- Identical active ingredient
- Same weight loss results
- Same side effects
- Same administration
Different:
- Cost: 67-85% cheaper
- Availability: Better supply
- Insurance: Compounded rarely covered
- Format: May be vials vs pens
Who Qualifies for GLP-1 Treatment?
GLP-1 weight loss medications are approved for specific patient populations based on BMI and health conditions.
FDA-Approved Eligibility Criteria:
Primary Qualification (BMI-Based):
You qualify if:
- BMI ≥30 (obesity category), OR
- BMI ≥27 (overweight category) PLUS at least one weight-related health condition
BMI Reference Guide:
| Height | BMI 27 Weight | BMI 30 Weight |
| 5’0″ | 140 lbs | 153 lbs |
| 5’2″ | 150 lbs | 164 lbs |
| 5’4″ | 158 lbs | 175 lbs |
| 5’6″ | 167 lbs | 186 lbs |
| 5’8″ | 177 lbs | 197 lbs |
| 5’10” | 186 lbs | 209 lbs |
| 6’0″ | 196 lbs | 221 lbs |
| 6’2″ | 206 lbs | 233 lbs |
Weight-Related Health Conditions (For BMI 27-29.9):
Qualifying conditions include:
- Type 2 diabetes or prediabetes
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- High cholesterol or dyslipidemia
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Cardiovascular disease
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Osteoarthritis exacerbated by weight
If you have BMI 27-29.9 with any of these conditions, you qualify.
Age Requirements:
FDA-Approved Ages:
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): Age 12 and older
- Tirzepatide (Zepbound): Age 18 and older
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): Age 12 and older
Adolescent Use:
- Increasingly prescribed for teens with obesity
- Requires pediatric endocrinologist oversight
- Family involvement in treatment plan
- Emphasis on lifestyle changes alongside medication
Absolute Contraindications (Cannot Use GLP-1s):
You CANNOT use GLP-1 medications if you have:
Personal or Family History of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC):
- Animal studies showed thyroid tumors with GLP-1s
- Not confirmed in humans but black box warning exists
- Absolute contraindication due to potential risk
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome Type 2 (MEN 2):
- Genetic condition predisposing to certain tumors
- Increases MTC risk
- GLP-1s contraindicated
Pregnancy or Planning Pregnancy:
- Animal studies showed fetal harm
- Stop medication 2 months before trying to conceive
- Cannot use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Previous Severe Allergic Reaction to GLP-1 Medications:
- Anaphylaxis or severe reaction to same class
- Risk of recurrence too high
Relative Contraindications (Use with Caution):
Discuss carefully with provider if you have:
History of Pancreatitis:
- GLP-1s may increase pancreatitis risk
- Prior pancreatitis is relative contraindication
- Some providers won’t prescribe, others use with close monitoring
Severe Gastroparesis:
- GLP-1s slow stomach emptying
- May worsen severe gastroparesis
- Mild gastroparesis may be okay with monitoring
History of Eating Disorders:
- Anorexia or bulimia history
- Medication-induced appetite suppression may trigger relapse
- Requires careful psychological screening
Severe Kidney Disease:
- Dehydration from nausea/vomiting can affect kidneys
- Close monitoring necessary
- May need dose adjustments
Active Gallbladder Disease:
- Rapid weight loss increases gallstone risk
- Existing gallbladder problems may worsen
- Monitor closely or address before starting
Diabetic Retinopathy:
- Rapid blood sugar improvement may temporarily worsen retinopathy
- Requires ophthalmology monitoring
- Not a contraindication but needs caution
Who Is a Good Candidate:
Ideal GLP-1 Patient:
- BMI ≥30 or BMI ≥27 with comorbidities
- Previous weight loss attempts unsuccessful
- No contraindications
- Realistic expectations
- Willing to commit to lifestyle changes
- Can afford treatment long-term
- Comfortable with weekly injections
- Motivated to improve health
Good Candidates Also Include:
Type 2 Diabetics:
- Benefit from blood sugar control plus weight loss
- May reduce other diabetes medications
- Cardiovascular benefits (semaglutide proven)
Cardiovascular Disease Patients:
- Semaglutide reduces heart attack/stroke risk
- Weight loss improves cardiovascular health
- Beneficial for prevention and treatment
Prediabetics:
- 60-70% reduction in diabetes progression
- Prevent full-blown diabetes
- Improve metabolic health
PCOS Patients:
- Weight loss improves PCOS symptoms
- Better insulin sensitivity
- May improve fertility
Who May Not Be Good Candidates:
Consider Alternatives If:
BMI <27 Without Comorbidities:
- Not FDA-approved indication
- Most providers won’t prescribe
- Focus on lifestyle modifications
Very Advanced Age:
- Frailty concerns
- Muscle loss risks with rapid weight loss
- Individual assessment needed
Active Cancer Treatment:
- Nausea from GLP-1s may compound chemotherapy side effects
- Weight loss may be detrimental during treatment
- Discuss with oncologist
Severe Psychiatric Conditions:
- Eating disorders (anorexia, bulimia)
- Active suicidal ideation
- Severe depression without treatment
- Psychiatric clearance may be needed
Financial Inability to Sustain Treatment:
- GLP-1s require long-term use
- Stopping leads to weight regain
- Must be able to afford medication for 18-24+ months
- Compounded options make this more accessible
Special Populations:
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
- Do not use during pregnancy
- Stop 2 months before trying to conceive
- Unknown if passes into breast milk
- Avoid during breastfeeding
Children and Adolescents:
- Wegovy approved age 12+
- Requires pediatric obesity specialist
- Family-based approach
- Growing evidence of safety and effectiveness
Elderly Patients:
- Can use with caution
- Monitor for muscle loss
- Ensure adequate protein intake
- More careful dose escalation
Bariatric Surgery Patients:
- Can use GLP-1s after surgery
- May help if weight regain occurs
- Enhances surgical results
- Increasingly common combination
Qualification Checklist:
Use this checklist to assess if you qualify:
- BMI ≥30, or BMI ≥27 with weight-related condition
- Age 18+ (12+ for some medications)
- No personal/family history of MTC or MEN 2
- Not pregnant or planning pregnancy soon
- No severe GLP-1 allergy history
- No active pancreatitis
- No severe eating disorder
- Can commit to long-term treatment
- Comfortable with weekly injections
- Have realistic expectations
If you checked all boxes, you likely qualify. Consult with a provider to confirm.
TrimRx providers can assess your eligibility during an online consultation and determine if GLP-1 therapy is appropriate for you.
Expected Results and Timeline
Understanding realistic outcomes and timeframes helps set appropriate expectations for GLP-1 therapy.
Average Weight Loss Results:
Semaglutide (Wegovy, Ozempic):
- Average: 10-15% of body weight lost
- Best case: 15-20% of body weight lost
- Minimum responders: 5-10% of body weight lost
- Timeline: 68 weeks (16 months) to maximum
Tirzepatide (Zepbound, Mounjaro):
- Average: 15-22% of body weight lost
- Best case: 25-30% of body weight lost
- Minimum responders: 10-15% of body weight lost
- Timeline: 72 weeks (18 months) to maximum
Real-World Examples:
200-Pound Person:
| Starting Weight | Medication | Average Loss | Final Weight |
| 200 lbs | Semaglutide | 30 lbs (15%) | 170 lbs |
| 200 lbs | Tirzepatide | 40 lbs (20%) | 160 lbs |
250-Pound Person:
| Starting Weight | Medication | Average Loss | Final Weight |
| 250 lbs | Semaglutide | 37 lbs (15%) | 213 lbs |
| 250 lbs | Tirzepatide | 50 lbs (20%) | 200 lbs |
300-Pound Person:
| Starting Weight | Medication | Average Loss | Final Weight |
| 300 lbs | Semaglutide | 45 lbs (15%) | 255 lbs |
| 300 lbs | Tirzepatide | 60 lbs (20%) | 240 lbs |
Month-by-Month Timeline:
Months 1-2: Getting Started
What Happens:
- Start at lowest dose (0.25 mg semaglutide or 2.5 mg tirzepatide)
- Body adjusts to medication
- Appetite begins decreasing
- Side effects most noticeable
Expected Weight Loss:
- 3-5 pounds
- Mostly water weight initially
- Some fat loss beginning
What to Expect:
- Reduced hunger between meals
- Smaller portions satisfying
- Some nausea or GI discomfort
- Learning injection technique
Months 3-4: Momentum Builds
What Happens:
- Dose increases to 0.5 mg semaglutide or 5 mg tirzepatide
- Appetite suppression more pronounced
- Side effects typically improving
- Weight loss accelerating
Expected Weight Loss:
- 8-12 pounds total (5-7 pounds these 2 months)
- 1-2 pounds per week
- Visible changes beginning
What to Expect:
- Consistent appetite control
- Easier to stick to healthy eating
- More energy as weight decreases
- Clothes fitting differently
Months 5-6: Steady Progress
What Happens:
- Dose increases to 1.0 mg semaglutide or 7.5 mg tirzepatide
- Sustained weight loss
- New habits forming
- Results becoming obvious
Expected Weight Loss:
- 15-20 pounds total (7-8 pounds these 2 months)
- 1.5-2 pounds per week
- 8-10% of starting weight lost
What to Expect:
- Significant visible changes
- Need smaller clothing sizes
- Improved energy and mobility
- Lab improvements (if checked)
- Family/friends noticing changes
Months 7-12: Continued Loss
What Happens:
- Dose increases to 1.7-2.4 mg semaglutide or 10-15 mg tirzepatide
- Approaching maintenance dose
- Weight loss continues steadily
- Metabolic benefits maximizing
Expected Weight Loss:
- 25-35 pounds total (10-15 pounds these 6 months)
- 1-1.5 pounds per week
- 12-17% of starting weight lost
What to Expect:
- Substantial transformation
- Multiple clothing sizes smaller
- Improved health markers
- Better physical function
- Sustained appetite control
Months 13-20: Reaching Maximum
What Happens:
- At maintenance dose
- Weight loss continuing but slower
- Approaching maximum loss
- Maintaining new weight becoming focus
Expected Weight Loss:
- 30-50+ pounds total (5-15 pounds these months)
- 0.5-1 pound per week
- 15-22% of starting weight lost (depending on medication)
What to Expect:
- Final weight stabilizing
- Focus on maintaining
- Lifestyle changes solidified
- Dramatic overall transformation
Factors Affecting Results:
Why Some People Lose More:
- Start at higher weight (more to lose)
- Strictly follow lifestyle recommendations
- Reach higher medication doses
- Excellent medication adherence
- Good side effect tolerance
- Genetic factors (responder status)
Why Some People Lose Less:
- Can’t tolerate higher doses due to side effects
- Inconsistent medication adherence
- Don’t implement lifestyle changes
- Have conditions affecting metabolism (hypothyroidism, PCOS)
- Genetic factors (lower responder)
- Medications interfering with weight loss
Individual Variation:
“Responder” Spectrum:
Super Responders (10-15% of patients):
- Lose 25-30% of body weight
- Excellent tolerance of maximum doses
- Dramatic appetite suppression
- May lose more than clinical trial averages
Average Responders (70-80% of patients):
- Lose 15-22% with tirzepatide, 10-15% with semaglutide
- Experience typical side effects
- Reach maintenance doses successfully
- Match clinical trial averages
Low Responders (10-15% of patients):
- Lose 5-10% of body weight
- May have significant side effects limiting doses
- Moderate appetite suppression
- Below clinical trial averages
- May benefit from switching medications or adding interventions
You can’t predict which category you’ll fall into until you try the medication.
Plateaus Are Normal:
What to Expect:
- Initial rapid loss (first 3 months)
- Continued steady loss (months 4-12)
- Plateau period (months 13-18)
- Final adjustments (months 19-24)
Plateaus don’t mean failure:
- Natural part of weight loss
- Body adjusting to new weight
- May need dose optimization
- Continue medication to maintain loss
Non-Scale Victories:
Results Beyond the Number:
Even if weight loss is slower than hoped, patients experience:
- Reduced waist circumference: Lost inches even when scale stalls
- Better blood pressure: 5-10 mmHg reduction common
- Improved blood sugar: A1C reductions of 1-2 points
- Better cholesterol: 10-20% improvement in lipids
- Increased energy: From weight loss and metabolic improvements
- Improved mobility: Easier movement, less joint pain
- Better sleep: Improvement in sleep apnea
- Enhanced quality of life: Confidence, mood, relationships
These improvements matter regardless of exact pounds lost.
When to Expect Specific Benefits:
Within Weeks:
- Reduced appetite and cravings
- Better blood sugar control (if diabetic)
- Initial energy improvements
Within Months:
- Visible weight loss (10+ pounds)
- Blood pressure improvements
- Better mobility and exercise tolerance
- Clothing size changes
Within 6-12 Months:
- Major weight loss (20-40 pounds)
- Significant health marker improvements
- Dramatic appearance changes
- Potential medication reductions (diabetes, BP meds)
Long-Term (12-24 Months):
- Maximum weight loss achieved
- Sustained health improvements
- Reduced risk of obesity complications
- Better overall quality of life
Setting Realistic Goals:
Healthy Goal-Setting:
Instead of “I want to lose X pounds by Y date,” focus on:
- Process goals: “Take medication consistently every week”
- Behavior goals: “Eat protein at every meal”
- Health goals: “Lower my A1C to non-diabetic range”
- Function goals: “Be able to walk 3 miles comfortably”
Weight goals should be:
- 10-15% of starting weight minimum (clinically significant)
- 15-25% of starting weight aspirational
- Flexible timelines (16-24 months)
- Focused on health improvements, not just numbers
Understanding how to buy semaglutide online safely ensures you get legitimate medication that produces these expected results.
Side Effects and Safety Information
GLP-1 medications are generally well-tolerated, but understanding potential side effects helps you prepare and manage them effectively.
Common Side Effects (Experienced by 20%+ of Patients):
Gastrointestinal Effects:
Nausea:
- Frequency: 30-44% depending on medication
- When: Most common during dose increases
- Duration: Usually peaks within 2-3 days of injection, improves by day 5-6
- Timeline: Most severe first 2 months, significantly better by month 3-4
Management:
- Eat smaller, frequent meals
- Avoid fatty, greasy, spicy foods
- Stay hydrated with clear fluids
- Ginger tea or ginger candies
- Inject before bed (sleep through worst nausea)
- Anti-nausea medication if severe (ondansetron, promethazine)
Diarrhea:
- Frequency: 19-30% of patients
- Usually mild to moderate
- Often improves after first month
Management:
- Increase fiber gradually
- Stay hydrated with electrolyte drinks
- Avoid trigger foods (dairy, caffeine, high-fat)
- Probiotics may help
- Anti-diarrheal medication if severe (loperamide)
Constipation:
- Frequency: 10-24% of patients
- Due to slowed GI transit
Management:
- Increase water intake (64-80 oz daily)
- Add fiber-rich foods
- Regular physical activity
- Stool softeners if needed (docusate)
- Magnesium supplements
- Miralax for occasional use
Vomiting:
- Frequency: 9-24% of patients
- Less common than nausea
- Usually during dose escalation
Management:
- Same strategies as nausea
- May need to slow dose escalation
- Contact provider if can’t keep fluids down
Abdominal Discomfort:
- Frequency: 8-20% of patients
- Usually mild bloating or cramping
- Related to slowed digestion
Management:
- Smaller portions
- Avoid gas-producing foods
- Gentle movement after meals
- Heat pad for comfort
Other Common Side Effects:
Fatigue:
- Frequency: 10-15% of patients
- Often related to reduced calorie intake
Management:
- Ensure adequate protein (80-100g daily)
- Don’t restrict calories too severely
- Regular sleep schedule
- Light exercise can boost energy
Headache:
- Frequency: 10-14% of patients
- Usually mild and temporary
Management:
- Stay hydrated
- OTC pain relievers (acetaminophen, ibuprofen)
- Usually resolves after first few weeks
Injection Site Reactions:
- Frequency: 5-10% of patients
- Mild redness, itching, or swelling
Management:
- Rotate injection sites
- Allow medication to reach room temperature before injecting
- Ice area before/after injection
- Usually resolves within days
Serious Side Effects (Rare but Important):
Pancreatitis:
- Risk: Less than 1% of patients
- Symptoms: Severe abdominal pain radiating to back, nausea, vomiting, fever
- Action: Stop medication immediately, seek emergency care
- Outcome: Usually resolves after discontinuation
Gallbladder Problems:
- Risk: 1-2% of patients
- Cause: Rapid weight loss increases gallstone risk
- Symptoms: Right upper abdominal pain, nausea, fever
- Action: Seek medical evaluation
- May require gallbladder removal in severe cases
Kidney Problems:
- Risk: Rare, usually from severe dehydration
- Symptoms: Decreased urination, swelling, confusion
- Prevention: Stay well-hydrated, especially during GI side effects
- Action: Contact provider if symptoms occur
Thyroid Tumors (Black Box Warning):
- Risk: Seen in animal studies, not confirmed in humans
- Absolute contraindication: Personal or family history of MTC or MEN 2
- Symptoms: Lump in neck, difficulty swallowing, persistent hoarseness
- Action: Report thyroid symptoms to provider immediately
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar):
- Risk: Low when GLP-1s used alone
- Higher risk: When combined with insulin or sulfonylureas
- Symptoms: Shakiness, sweating, confusion, dizziness, rapid heartbeat
- Prevention: Diabetes medication doses may need reduction
- Action: Treat with fast-acting carbs, contact provider about dose adjustments
Allergic Reactions:
- Risk: Very rare
- Symptoms: Difficulty breathing, facial swelling, severe rash, throat tightness
- Action: Seek emergency care immediately
- Contraindication for future use
Side Effect Timeline:
First Week:
- Mild nausea possible
- Reduced appetite begins
- GI changes starting
- Injection site learning curve
Weeks 2-4:
- Side effects may intensify
- Nausea peaks for many
- GI symptoms most noticeable
- Fatigue from calorie reduction
Weeks 5-8:
- Dose increase may temporarily worsen side effects
- But overall improvement from week 4
- Body adapting to medication
- Most patients feeling better
Weeks 9-12 and Beyond:
- Significant improvement in side effects
- GI symptoms mild or resolved
- Appetite suppression sustained
- Most patients tolerating well
For many patients, the worst side effects are weeks 2-6, with major improvement after 2 months.
Who Experiences More Side Effects:
Higher Risk of Side Effects:
- Women (higher rates than men)
- Starting at higher doses
- Rapid dose escalation
- History of GI issues (GERD, IBS)
- Slower metabolism
- Older age
Lower Risk of Side Effects:
- Men (lower rates than women)
- Gradual dose escalation
- Prior GLP-1 exposure
- Following dietary recommendations
Managing Side Effects Successfully:
Diet Modifications:
Foods to Emphasize:
- Lean proteins (chicken, fish, eggs)
- Non-starchy vegetables
- Clear broths and soups
- Crackers, toast (for nausea)
- Ginger (natural anti-nausea)
- Peppermint tea
Foods to Avoid:
- Fatty, greasy foods (worsen nausea)
- Spicy foods (irritate GI tract)
- Large portions (harder to digest)
- Carbonated drinks (increase bloating)
- Alcohol (worsens nausea, dehydration)
- High-sugar foods (blood sugar swings)
Eating Strategies:
- Small, frequent meals (5-6 times daily)
- Eat slowly, chew thoroughly
- Stop when satisfied (don’t push to full)
- Stay upright after eating (prevents reflux)
- Don’t drink large amounts with meals
When to Contact Your Provider:
Urgent (Call Immediately):
- Severe abdominal pain
- Persistent vomiting (can’t keep fluids down)
- Signs of dehydration (dark urine, dizziness, confusion)
- Severe allergic reaction
- Vision changes
- Symptoms of pancreatitis
Non-Urgent (Schedule Appointment):
- Side effects not improving after 4 weeks
- Want to discuss slowing dose escalation
- Questions about managing side effects
- Considering anti-nausea medication
- Weight loss plateau concerns
Discontinuation Rates:
Due to Side Effects:
- Semaglutide: 6.9% discontinue
- Tirzepatide: 6.2% discontinue
- Over 93% of patients tolerate well enough to continue
Long-Term Safety:
Semaglutide:
- On market since 2017 (8 years)
- Extensive real-world safety data
- SELECT trial: Actually reduced cardiovascular events (20% reduction)
- No new safety concerns with longer use
Tirzepatide:
- On market since 2022 (3 years)
- Growing real-world safety data
- Clinical trials show excellent safety profile
- Cardiovascular outcomes trial ongoing
Both medications appear safe for long-term use based on available evidence.
Drug Interactions:
Medications Requiring Monitoring:
Insulin and Sulfonylureas:
- GLP-1s may increase hypoglycemia risk
- Dose reductions usually needed
- Close blood sugar monitoring
Blood Thinners (Warfarin):
- GLP-1s may affect warfarin levels
- Monitor INR more frequently initially
Oral Medications:
- Slowed stomach emptying may affect absorption
- Take important medications 1 hour before GLP-1 injection
- Discuss timing with provider
Generally Compatible With:
- Blood pressure medications
- Cholesterol medications
- Most psychiatric medications
- Thyroid medications
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
Pregnancy:
- Do not use GLP-1s during pregnancy
- Animal studies showed potential fetal harm
- Stop medication 2 months before trying to conceive
- Use reliable contraception during treatment
Breastfeeding:
- Unknown if GLP-1s pass into breast milk
- Avoid use during breastfeeding
- Discuss alternatives with provider
Bottom Line on Safety:
GLP-1 medications are:
- ✓ Generally well-tolerated (93% continue treatment)
- ✓ Side effects usually manageable and improve over time
- ✓ Serious side effects rare (<2%)
- ✓ Safe for long-term use based on current evidence
- ✓ Benefits typically outweigh side effects for appropriate patients
Keys to success:
- Start at lowest dose
- Escalate gradually
- Follow dietary recommendations
- Stay hydrated
- Communicate with provider about side effects
- Don’t suffer unnecessarily—management strategies help
Learn about affordable Mounjaro alternatives that provide the same medication with the same side effect profile at lower cost.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
Understanding the full cost picture helps you budget for GLP-1 therapy and explore all available options.
Brand-Name Costs (Without Insurance):
Monthly List Prices:
- Wegovy (semaglutide): $1,349
- Ozempic (semaglutide): $969
- Zepbound (tirzepatide): $1,069
- Mounjaro (tirzepatide): $1,069
- Saxenda (liraglutide): $1,400
Annual Costs:
- Semaglutide: $11,628-$16,188/year
- Tirzepatide: $12,828/year
- For 18-month treatment: $17,442-$24,282
These prices are unsustainable for most cash-pay patients.
Insurance Coverage:
Coverage Likelihood:
Most Likely to Be Covered:
- Ozempic for type 2 diabetes (diabetes indication)
- Mounjaro for type 2 diabetes (diabetes indication)
Sometimes Covered:
- Wegovy for weight loss (if plan covers obesity treatment)
- Zepbound for weight loss (newer, fewer plans cover)
Rarely Covered:
- Weight loss medications on most plans
- Medicare/Medicaid don’t cover for weight loss (federal law)
Typical Copays (If Covered):
- Tier 2 (preferred): $25-$75/month
- Tier 3 (non-preferred): $100-$200/month
- Specialty tier: $200-$300/month or 25-33% coinsurance
Prior Authorization Requirements:
Insurance Typically Requires:
Documentation of:
- BMI ≥30 or BMI ≥27 with comorbidities (documented)
- Failed weight loss attempts (6-12 months documented diet/exercise)
- Medical necessity letter from provider
- No contraindications
May Also Require:
- Nutrition counseling documentation
- Exercise program participation
- Weight loss journal
- Commitment to lifestyle modifications
- Regular follow-up appointments
Timeline:
- Prior authorization: 1-4 weeks processing
- Appeals if denied: Additional 2-8 weeks
- No guarantee of approval
Manufacturer Savings Programs:
Eli Lilly (Mounjaro/Zepbound):
- Savings Card: May reduce cost to $25/month
- Requirements: Commercial insurance (not Medicare/Medicaid)
- Not available for: Uninsured cash-pay patients
- Income limits: May apply
Novo Nordisk (Wegovy/Ozempic):
- Savings Card: May reduce cost to $25/month
- Requirements: Commercial insurance (not Medicare/Medicaid)
- Not available for: Uninsured cash-pay patients
If you qualify for savings cards, brand-name medications become very affordable ($25-$50/month).
Compounded Medication Costs:
Monthly Pricing:
Semaglutide:
- TrimRx: $199/month with annual commitment
- Other providers: $199-$599/month
- Average: $300-$400/month
Tirzepatide:
- TrimRx: $349/month with annual commitment
- Other providers: $349-$699/month
- Average: $450-$550/month
What’s Included (TrimRx):
- Licensed provider consultation
- Prescription
- Medication from FDA-registered pharmacy
- All injection supplies (syringes, needles, alcohol pads, sharps container)
- Free shipping with cold-chain packaging
- Monthly follow-up appointments
- Access to medical support
Annual Costs:
- Semaglutide: $2,388-$7,188
- Tirzepatide: $4,188-$8,388
Insurance Coverage for Compounded:
- Insurance: Rarely covers compounded medications
- HSA/FSA: Usually eligible for compounded medications
- Payment: Out-of-pocket at time of service
Cost Comparison:
| Option | Monthly | Annual (18 mo) | Total 18 Mo |
| Brand Semaglutide (no insurance) | $1,349 | $16,188 | $24,282 |
| Brand Tirzepatide (no insurance) | $1,069 | $12,828 | $19,242 |
| Brand (with savings card) | $25-$50 | $300-$600 | $450-$900 |
| Brand (typical insurance) | $150-$250 | $1,800-$3,000 | $2,700-$4,500 |
| Compounded Semaglutide (TrimRx) | $199 | $2,388 | $3,582 |
| Compounded Tirzepatide (TrimRx) | $349 | $4,188 | $6,282 |
Hidden Costs to Consider:
Additional Expenses:
Medical Visits (If Not Included):
- Initial consultation: $150-$300
- Follow-up visits: $100-$200 each
- Required frequency: Monthly
Lab Work:
- Initial labs: $150-$300
- Periodic monitoring: $100-$200
- May be covered by insurance separately
Anti-Nausea Medication:
- If needed: $10-$50/month
- Usually temporary
Transportation:
- For in-person visits
- Parking fees
- Time off work
Telehealth Eliminates:
- Transportation costs
- Time off work
- Parking fees
- Often includes visits in monthly price
HSA/FSA Eligibility:
Can Use for:
- Compounded GLP-1 medications
- Brand-name medications (with prescription)
- Medical consultations
- Lab work
- Supplies
Tax Savings:
- Pre-tax dollars = 20-30% savings
- $199/month medication costs ~$140-$160 after tax benefit
- $349/month medication costs ~$245-$280 after tax benefit
Strategies to Reduce Costs:
- Try Insurance First:
- If you have insurance, attempt approval
- Savings cards may reduce to $25/month
- Worth the effort if potential for low copay
- But don’t wait months if denied—move to alternatives
- Use Compounded Medications:
- 67-85% cheaper than brand-name
- Same active ingredient and effectiveness
- TrimRx offers lowest pricing with full support
- Choose Annual Commitments:
- Many providers discount for longer commitments
- TrimRx pricing based on annual commitment
- Saves 15-30% vs month-to-month
- Use HSA/FSA Funds:
- Pre-tax savings of 20-30%
- Makes monthly cost more affordable
- Plan ahead to maximize HSA contributions
- Start with Semaglutide:
- Lower cost than tirzepatide ($199 vs $349)
- Still highly effective (10-15% weight loss)
- Can upgrade to tirzepatide later if desired
- Compare Multiple Providers:
- Pricing varies widely ($199-$699 for same medication)
- Check what’s included in price
- Verify pharmacy partners
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis:
Cost Per Pound Lost (18-Month Treatment):
| Option | Total Cost | Pounds Lost | Cost/Pound |
| Compounded Semaglutide | $3,582 | 37 | $97 |
| Compounded Tirzepatide | $6,282 | 56 | $112 |
| Brand Semaglutide (no ins) | $24,282 | 37 | $656 |
| Brand Tirzepatide (no ins) | $19,242 | 56 | $344 |
Compounded medications offer 6-7x better cost-effectiveness than brand-name for cash-pay patients.
Long-Term Budget Planning:
Plan For:
Active Weight Loss (18-24 months):
- Semaglutide: $3,582-$4,776
- Tirzepatide: $6,282-$8,376
Maintenance Phase (Indefinite):
- Same monthly cost continues
- May reduce to lower maintenance dose
- Budget for long-term treatment
Total 3-Year Cost:
- Semaglutide: $7,164
- Tirzepatide: $12,564
Financial Assistance:
If You Can’t Afford Treatment:
Options to Explore:
- Patient assistance programs (brand-name manufacturers)
- Community health centers (may offer reduced-cost programs)
- Clinical trials (free medication, but specific requirements)
- Flexible spending accounts (plan ahead for next year)
- Medical credit cards (CareCredit, etc. – use cautiously)
Making Treatment Sustainable:
Key Questions:
- Can I afford this for 18-24 months minimum?
- What happens if I need to stop due to cost?
- Is there a lower-cost option that still works?
- Can I use pre-tax dollars to reduce cost?
Weight regain after stopping makes long-term affordability crucial.
Bottom Line on Cost:
For Cash-Pay Patients:
- Best value: Compounded semaglutide at $199/month
- Maximum results: Compounded tirzepatide at $349/month
- Avoid: Brand-name at $1,000+/month (unsustainable)
With Good Insurance:
- Try savings cards: May get $25/month brand-name
- If high copays: Compounded may be cheaper
- Factor in: Total out-of-pocket including deductibles
Plan for long-term treatment costs—obesity is a chronic condition requiring sustained therapy.
Getting Started with GLP-1 Therapy
Ready to begin? Here’s your step-by-step guide to starting GLP-1 treatment safely and effectively.
Step 1: Determine Your Eligibility
Quick Self-Assessment:
Calculate Your BMI: BMI = (Weight in pounds / (Height in inches)²) × 703
Or use this quick reference:
- 5’4″, 175 lbs = BMI 30
- 5’6″, 186 lbs = BMI 30
- 5’8″, 197 lbs = BMI 30
- 5’10”, 209 lbs = BMI 30
You likely qualify if:
- ✓ BMI ≥30, OR
- ✓ BMI 27-29.9 + diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, or sleep apnea
- ✓ Age 18+ (12+ for some medications)
- ✓ No personal/family history of thyroid cancer
- ✓ Not pregnant or planning pregnancy
If you meet these criteria, proceed to Step 2.
Step 2: Choose Your Approach
Option A: Through Insurance
Best for: People with insurance that might cover
Process:
- Check if your plan covers Wegovy or Zepbound
- Contact insurance about requirements
- See in-network provider
- Complete prior authorization
- If approved with low copay, use insurance
- If denied or copay too high, consider Option B
Timeline: 2-8 weeks Cost if successful: $25-$300/month
Option B: Compounded Through Telehealth
Best for: Cash-pay patients, high insurance copays, want immediate access
Process:
- Choose reputable provider (TrimRx)
- Complete online consultation
- Get prescription same day if approved
- Medication ships in 3-7 days
- Start treatment
Timeline: 3-7 days total Cost: $199-$349/month
Most people find Option B faster, easier, and more affordable.
Step 3: Complete Medical Consultation
Information You’ll Provide:
Medical History:
- Current height and weight
- Medical conditions (diabetes, hypertension, thyroid issues, etc.)
- Current medications and supplements
- Allergies
- Family history (especially thyroid cancer)
- Previous weight loss attempts
- Surgical history
Current Health:
- Recent blood pressure
- Latest lab work (if available)
- Current symptoms
- Pregnancy status
Lifestyle:
- Diet patterns
- Exercise habits
- Stress levels
- Sleep quality
- Support system
Be completely honest—accurate information ensures safe prescribing.
Consultation Format:
Asynchronous (Most Common):
- Complete detailed questionnaire online
- Provider reviews within 24-48 hours
- Responds with questions or approval
- Can message with questions
Live Video/Phone:
- Scheduled appointment (15-30 minutes)
- Real-time discussion with provider
- Ask questions directly
- Decision made during visit
What Provider Assesses:
- Eligibility for GLP-1 therapy
- Which medication is best for you
- Starting dose
- Contraindications
- Realistic expectations
- Commitment to treatment
Step 4: Choose Your Medication
Decision Framework:
Choose Semaglutide If:
- Want excellent results at lowest cost
- Need to lose 20-50 pounds
- Budget is primary concern ($199/month)
- Have cardiovascular disease
Choose Tirzepatide If:
- Want maximum results
- Need to lose 50+ pounds
- Can afford $349/month
- Want most effective medication
Your provider will help you decide based on your goals, health status, and budget.
Step 5: Receive Your Medication
What Arrives:
Package Contents:
- Medication vials or syringes
- Syringes and needles (if using vials)
- Alcohol prep pads
- Sharps container for safe needle disposal
- Instruction guide
- Storage information
Immediate Actions:
- Verify package arrived cold (ice packs present)
- Check medication appearance (should be clear, colorless)
- Confirm expiration/beyond-use date
- Store in refrigerator immediately (36-46°F)
- Don’t freeze
- Keep in original packaging
Step 6: Prepare for First Injection
Before Your First Dose:
Watch Training Video:
- Most providers supply injection tutorials
- See technique demonstrated
- Learn proper steps
- Review safety measures
Gather Supplies:
- Medication from refrigerator (can sit at room temp 15-30 min)
- Syringe and needle (if using vial)
- Alcohol prep pad
- Sharps container
- Cotton ball or gauze (optional)
Choose Injection Site:
- Abdomen (2+ inches from belly button)
- Front/side of thigh
- Back of upper arm (may need help)
- Rotate sites each week
Step 7: Administer First Injection
Injection Steps:
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water
- Prepare injection site
- Clean with alcohol pad
- Let air dry (don’t blow on it)
- Prepare medication
- If using vial: Draw prescribed dose into syringe
- If using pre-filled syringe: Remove cap
- Check for air bubbles, tap syringe to remove
- Pinch skin gently between thumb and fingers
- Insert needle at 90-degree angle
- Quick, dart-like motion
- Needle should go fully under skin
- Inject medication
- Push plunger slowly and steadily
- Hold for 5 seconds after injecting
- Remove needle
- Pull straight out
- Release pinched skin
- Apply gentle pressure if needed
- Dispose of needle
- Place directly into sharps container
- Never recap needle
First Injection Tips:
- Take your time—no need to rush
- Most people find it much easier than expected
- Needle is very small and thin
- Quick insertion hurts less than slow
- Contact provider support if you need help
Step 8: Manage First Week
What to Expect:
Days 1-2:
- May not notice much initially
- Medication building up in system
- Continue eating normally
Days 3-5:
- Appetite may start decreasing
- Food might sound less appealing
- Some mild nausea possible
Days 6-7:
- Reduced hunger more noticeable
- Smaller portions satisfying
- First pounds of weight loss (water weight)
Managing Early Side Effects:
For Nausea:
- Eat smaller, frequent meals
- Choose bland, easy-to-digest foods
- Avoid fatty and spicy foods
- Ginger tea helps
- Stay hydrated
For Fatigue:
- Don’t restrict calories too much
- Ensure adequate protein
- Get regular sleep
- Light activity helps
For GI Upset:
- Increase fiber gradually
- Stay hydrated
- Avoid trigger foods
- Usually improves within weeks
Step 9: Establish Your Routine
Weekly Injection Schedule:
Pick Same Day Each Week:
- Choose a day that works for your schedule
- Many prefer Sunday evening (forget about it all week)
- Set phone reminder
- Can inject same day ±2 days if needed
Create Routine:
- Set medication out 30 minutes early (room temp comfort)
- Prepare injection area
- Inject at same general time
- Track in calendar or app
- Note any side effects
Lifestyle Practices:
Nutrition:
- Prioritize protein (20-30g per meal)
- Eat vegetables with every meal
- Stay hydrated (64+ oz water daily)
- Avoid drinking calories
- Listen to hunger cues
Physical Activity:
- Start with daily walking (30 minutes)
- Add strength training 2-3x/week
- Preserve muscle during weight loss
- Gradually increase as weight decreases
Tracking:
- Weekly weigh-ins (same day, same time)
- Measurements (waist, hips)
- Progress photos (monthly)
- How you feel (energy, mobility)
- Non-scale victories
Step 10: Attend Follow-Up Appointments
Typical Schedule:
Week 2:
- Check in on side effects
- Review injection technique
- Answer questions
- Assess initial tolerance
Month 1:
- First dose increase (if tolerating well)
- Review weight loss progress
- Adjust management strategies
- Prescription refill
Monthly Thereafter:
- Continue dose escalation
- Monitor progress toward goals
- Manage any issues
- Optimize treatment
Between Appointments:
- Message provider with questions
- Report concerning side effects
- Request help if struggling
- Update on any health changes
Troubleshooting Common Early Issues:
“I’m Not Losing Weight Yet”
- Normal in first 2-3 weeks
- Takes time to reach therapeutic levels
- Weight loss accelerates as dose increases
- Be patient
“The Nausea Is Really Bad”
- Contact provider about anti-nausea medication
- May slow down dose escalation
- Try dietary modifications
- Usually improves significantly by week 6-8
“I Forgot My Injection”
- Take as soon as you remember if within 5 days
- If more than 5 days late, skip and take next dose on schedule
- Don’t double up
- Set reminders to prevent forgetting
“I Don’t Like Injections”
- Use numbing cream before injection (topical lidocaine)
- Inject slowly to reduce discomfort
- Distract yourself during injection
- Gets easier with practice
- Most people adjust within 2-3 weeks
Success Tips:
For Best Results:
- ✓ Take medication consistently every week
- ✓ Follow dietary recommendations
- ✓ Stay physically active
- ✓ Attend all follow-up appointments
- ✓ Communicate openly with provider
- ✓ Be patient with timeline (16-20 months)
- ✓ Focus on non-scale victories too
- ✓ Commit to long-term treatment
Avoid:
- ✗ Skipping doses
- ✗ Ignoring side effects that persist
- ✗ Expecting rapid results (takes time)
- ✗ Relying solely on medication (combine with lifestyle)
- ✗ Stopping too soon
- ✗ Comparing your results to others
When to Contact Provider:
Urgent:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Can’t keep fluids down
- Signs of allergic reaction
- Vision changes
- Severe side effects
Non-Urgent but Important:
- Side effects not improving after 4 weeks
- Questions about dose escalation
- Weight loss concerns
- Need anti-nausea medication
- General questions about treatment
Ready to Start?
TrimRx makes starting GLP-1 therapy simple:
- Complete online health assessment (10 minutes)
- Consult with licensed provider (24-48 hours)
- Medication ships to your door (3-7 days)
- Begin your weight loss journey with full support
Choose your medication:
Both include licensed medical consultations, all supplies, free shipping, and ongoing support.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is GLP-1 therapy for weight loss? GLP-1 therapy uses medications that mimic a natural hormone your body produces to regulate appetite and blood sugar. These medications (semaglutide and tirzepatide) are injected once weekly and produce 10-22% average body weight loss by reducing hunger, increasing feelings of fullness, and slowing digestion. GLP-1 therapy is the most effective weight loss medication treatment available, producing results previously only achievable through bariatric surgery.
How much weight can you lose with GLP-1 medications? With semaglutide (Wegovy, Ozempic), patients lose an average of 10-15% of body weight (25-37 pounds for a 250-pound person) over 16-18 months. With tirzepatide (Zepbound, Mounjaro), patients lose an average of 15-22% of body weight (37-55 pounds for a 250-pound person) over 18-20 months. Individual results vary, but 85-95% of patients lose at least 5% of their body weight.
Do GLP-1 medications require injections? Yes, the most effective GLP-1 medications (semaglutide and tirzepatide) are once-weekly subcutaneous injections using very small, thin needles. The injections are much easier than most people expect—similar to a quick pinch. An oral form of semaglutide (Rybelsus) exists but is significantly less effective (3-5% weight loss vs 10-15% with injections). Most patients find weekly injections preferable to daily pills.
What are the most common side effects of GLP-1 therapy? The most common side effects are gastrointestinal: nausea (30-44%), diarrhea (19-30%), constipation (10-24%), and occasional vomiting (9-24%). These side effects are usually most noticeable during the first 2 months and improve significantly by weeks 6-8. Most patients (93%) tolerate side effects well enough to continue treatment. Strategies like eating smaller meals, avoiding fatty foods, and taking anti-nausea medication help manage symptoms.
How much does GLP-1 weight loss therapy cost? Brand-name medications cost $969-$1,349/month without insurance. With insurance coverage and savings cards, copays may be $25-$300/month. Compounded GLP-1 medications cost significantly less: semaglutide averages $199-$599/month (TrimRx: $199/month), and tirzepatide averages $349-$699/month (TrimRx: $349/month). Compounded options provide the same active ingredient at 67-85% lower cost.
Do you have to stay on GLP-1 medications forever? Most patients need long-term or indefinite treatment to maintain weight loss. Clinical trials show that stopping GLP-1 medications leads to weight regain for most people—patients regained 2/3 of lost weight within one year of stopping. Obesity is a chronic condition, and GLP-1 medications treat the underlying biology. Think of it like blood pressure or diabetes medication—ongoing treatment manages a chronic condition rather than curing it.
Can I get GLP-1 medications through telehealth? Yes, licensed telehealth providers can prescribe GLP-1 medications after appropriate medical evaluation. TrimRx offers complete online service including consultations with licensed providers, prescriptions, and medication delivery to your door—all without requiring in-person visits. This makes GLP-1 therapy accessible regardless of your location or ability to visit weight loss clinics in person.
Which is better: semaglutide or tirzepatide? Tirzepatide produces superior weight loss (15-22% vs 10-15% with semaglutide) due to its dual GIP/GLP-1 mechanism. However, semaglutide costs less (compounded: $199 vs $349/month), has proven cardiovascular benefits, and longer safety track record. Choose tirzepatide for maximum weight loss or semaglutide for excellent results at lower cost. Compare both medications in detail.
Who should not take GLP-1 medications? GLP-1 medications are contraindicated for people with personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). They should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Use caution if you have history of pancreatitis, severe gastroparesis, or eating disorders. Consult a provider to determine if GLP-1 therapy is safe for your specific situation.
How long does it take to see results with GLP-1 therapy? Most people notice reduced appetite within 1-2 weeks of starting. Measurable weight loss typically begins by weeks 3-4 (3-5 pounds). Significant weight loss becomes apparent by months 3-6 (15-25 pounds) and continues for 16-20 months until reaching maximum results. Weight loss is gradual and sustained rather than rapid—expect to lose 1-2 pounds per week on average once therapeutic doses are reached.
Ready to begin your GLP-1 weight loss journey? TrimRx provides accessible, affordable access to compounded semaglutide at $199/month and compounded tirzepatide at $349/month with licensed medical oversight, FDA-registered pharmacy partners, and complete support.

Transforming Lives, One Step at a Time
Keep reading
GLP-1 Telehealth on the West Coast: CA, WA and OR
The West Coast has a reputation for progressive healthcare policy and high insurance coverage rates, and in many respects that reputation is earned. California,…
GLP-1 Telehealth in the Southwest: TX, AZ, NV and NM
The Southwest is a region of stark contrasts when it comes to healthcare access. Phoenix and Las Vegas are sprawling, fast-growing metros with expanding…
GLP-1 Telehealth in the Midwest: IL, OH, MI and IN
The Midwest doesn’t get as much attention in conversations about obesity and healthcare access as the South does, but the numbers tell a sobering…



